Ocean Conservation
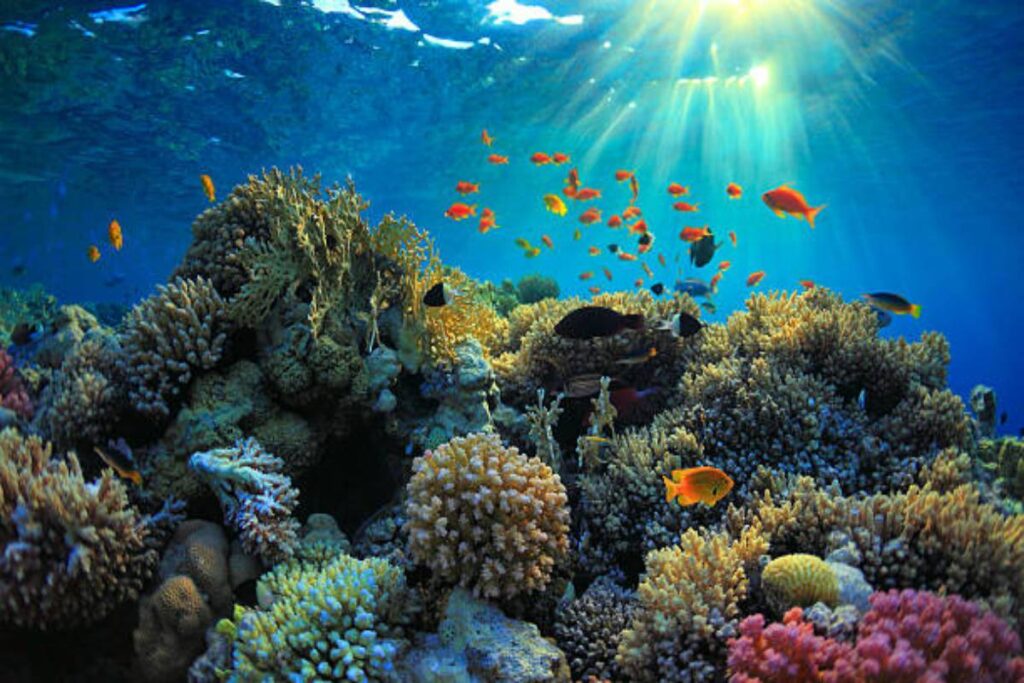

Introduction
Our planet’s health is derived from its tremendous and seemingly endless oceans. Providing a rich tapestry of marine life, they span more than 70% of Earth’s surface, control our climate, and generate a substantial amount of oxygen for human use. Unfortunately, a number of risks to this essential resource threaten the health of our seas and, by extension, the health of our planet.
Ocean Conservation: Why It Matters
Maintaining and safeguarding the wellbeing and variety of life in our waters is known as ocean conservation. It includes, among other things, establishing marine protected zones, encouraging sustainable fishing methods, and combating issues like plastic waste and overfishing.
Ocean Conservation: Protecting Our Blue Planet
Oceans cover more than 70% of our planet’s surface, playing a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate, providing food and livelihoods for millions of people, and supporting a vast array of marine life. However, these invaluable ecosystems are facing unprecedented threats due to human activities. Ocean conservation is paramount to safeguarding the health and vitality of our oceans for future generations.
Understanding the Threats
Pollution really is an issue:
Pollution from sources such as plastic waste, oil spills, chemical runoff, and marine debris really poses a significant threat to ocean health. It harms marine life, disrupts ecosystems, and affects human health through contaminated seafood and polluted beaches.

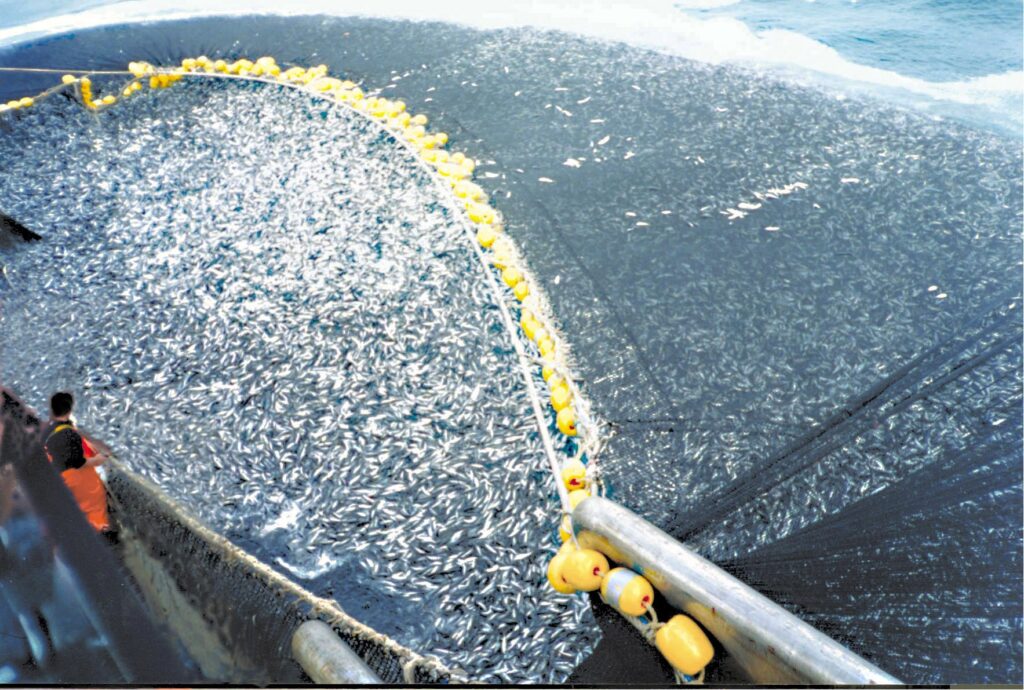
Overfishing is very problematic:
Overfishing really depletes fish stocks, disrupts marine food webs, and threatens the livelihoods of coastal communities that depend on fishing for their sustenance. Unsustainable fishing practices can lead to the collapse of fish populations and irreversible damage to marine ecosystems.

Habitat Destruction cannot be overlooked:
Human activities such as coastal development, dredging, and bottom trawling really destroy critical marine habitats such as coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrass beds. These habitats serve as breeding grounds and nurseries for marine species, and their destruction can have far-reaching consequences for ocean biodiversity.
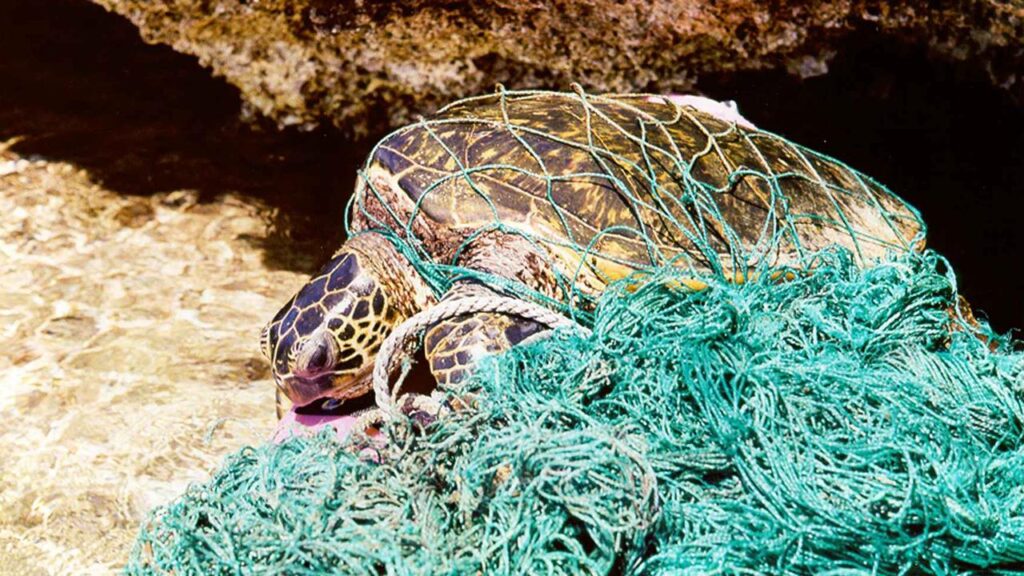

Climate Change is a big problem:
Climate change really exacerbates existing threats to oceans, leading to phenomena such as ocean acidification, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events. These impacts disrupt marine ecosystems, endanger species, and undermine the resilience of coastal communities.
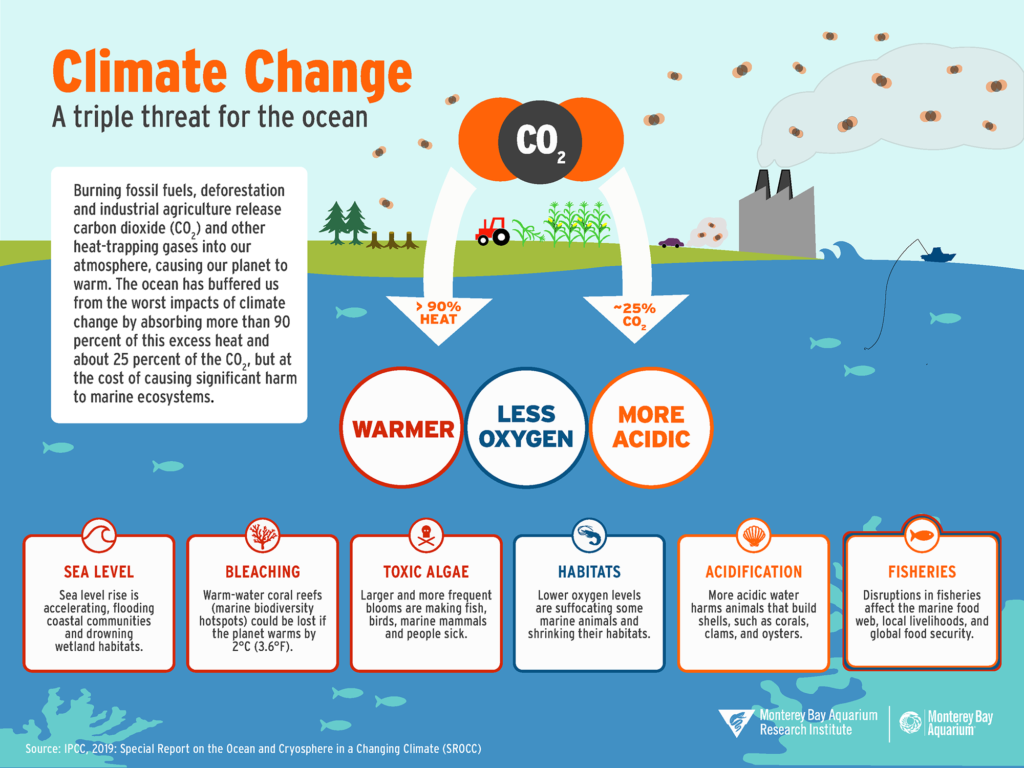
Strategies for Conservation
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
MPAs are designated areas where human activities are regulated to conserve marine biodiversity and habitats. They serve as sanctuaries for marine life, allowing ecosystems to recover and thrive. - Sustainable Fisheries Management:
Implementing regulations and practices to ensure fish populations are harvested sustainably is essential for maintaining healthy oceans and vibrant fisheries. This includes setting catch limits, protecting spawning grounds, and promoting responsible fishing practices. - Reduction of Pollution:
Efforts to reduce pollution in oceans involve implementing policies to minimize plastic waste, improving waste management systems, and promoting recycling and waste reduction initiatives. - Climate Change Mitigation:
Addressing the root causes of climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, is crucial for mitigating its impacts on ocean ecosystems. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and protecting carbon sinks such as mangroves and salt marshes. - Community Engagement and Education:
Raising awareness about the importance of ocean conservation and empowering communities to participate in conservation efforts is essential for building public support and fostering stewardship of marine resources. - Technological Innovation:
Advances in technology, such as satellite monitoring, underwater drones, and genetic monitoring, are revolutionizing ocean conservation efforts by providing valuable data for research, monitoring, and management. - International Collaboration:
Collaboration among governments, NGOs, scientists, and stakeholders at local, national, and international levels is essential for addressing transboundary challenges and promoting sustainable ocean management.
Success Stories and Future Directions
- Role of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
MPAs have been instrumental in protecting and restoring marine ecosystems worldwide. Success stories include the recovery of fish populations, restoration of coral reefs, and conservation of endangered species. - Sustainable Fisheries Management:
Countries that have implemented sustainable fisheries management practices have seen improvements in fish stocks, ecosystem health, and economic benefits for fishing communities. - Addressing Pollution:
Efforts to reduce plastic pollution, such as bans on single-use plastics and cleanup initiatives, have yielded positive results in some regions, highlighting the effectiveness of targeted interventions. - Mitigating Climate Change Effects:
Investments in renewable energy, coastal adaptation measures, and ecosystem-based approaches to climate change mitigation are critical for safeguarding oceans from the impacts of climate change.
Challenges and Future Directions:
- Despite progress in ocean conservation efforts, significant challenges remain, including inadequate funding, lack of political will, and gaps in enforcement and compliance. Addressing these challenges requires sustained commitment and collaboration from all stakeholders.
Conclusion:
Ocean conservation is a shared responsibility that requires collective action to protect and preserve our blue planet. By implementing strategies such as marine protected areas, sustainable fisheries management, pollution reduction, and climate change mitigation, we can ensure the health and vitality of oceans for future generations to enjoy.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What are some simple actions individuals can take to support ocean conservation?
- Reduce plastic consumption
- Dispose of waste properly
- Support sustainable seafood choices
- Participate in beach cleanups and conservation initiatives
- How does ocean conservation contribute to the economy?
- Healthy oceans support industries such as fishing, tourism, and recreation, providing jobs and economic opportunities for coastal communities.
- What role do governments play in ocean conservation?
- Governments enact policies and regulations to protect marine environments.

4 thoughts on “Ocean Conservation”
I truly wanted to write a brief message so as to express gratitude to you for these amazing advice you are giving here. My considerable internet lookup has now been honored with good concept to go over with my neighbours. I would repeat that many of us readers are extremely lucky to live in a remarkable website with many awesome professionals with good guidelines. I feel rather fortunate to have seen the weblog and look forward to plenty of more awesome times reading here. Thanks a lot again for a lot of things.
You are a very bright individual!
I’m really impressed with your writing abilities as neatly as with the structure in your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Either way stay up the nice quality writing, it抯 rare to peer a great blog like this one nowadays..
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?