What is Biosphere Reserve ?
INTRODUCTION:
In an era where human activities increasingly impact the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems, the concept of biosphere reserves emerges as a beacon of hope for the coexistence of nature and development. Designated by UNESCO, these protected areas are uniquely poised to conserve biodiversity while promoting sustainable practices. In this blog, we will delve into the world of biosphere reserves, exploring their significance, features, and the crucial role they play in safeguarding our planet’s future.
Biosphere Reserve
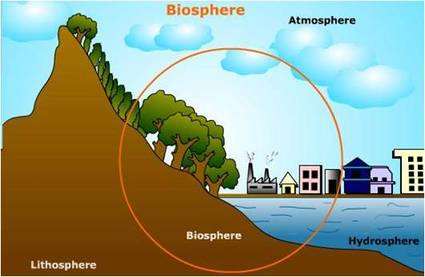
A biosphere reserve is an area of land, water, or a combination of both that is designated by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to promote the conservation of biodiversity while also supporting sustainable development. Biosphere reserves are intended to balance the needs of conservation, research, and economic development, all within a single protected area.
The Essence of Biosphere Reserves:
Biosphere reserves represent a pioneering approach to conservation, recognizing that humans are an integral part of the environment and their sustainable development is essential for the well-being of both nature and society. These reserves aim to strike a delicate balance between biodiversity conservation, research, education, and economic development.
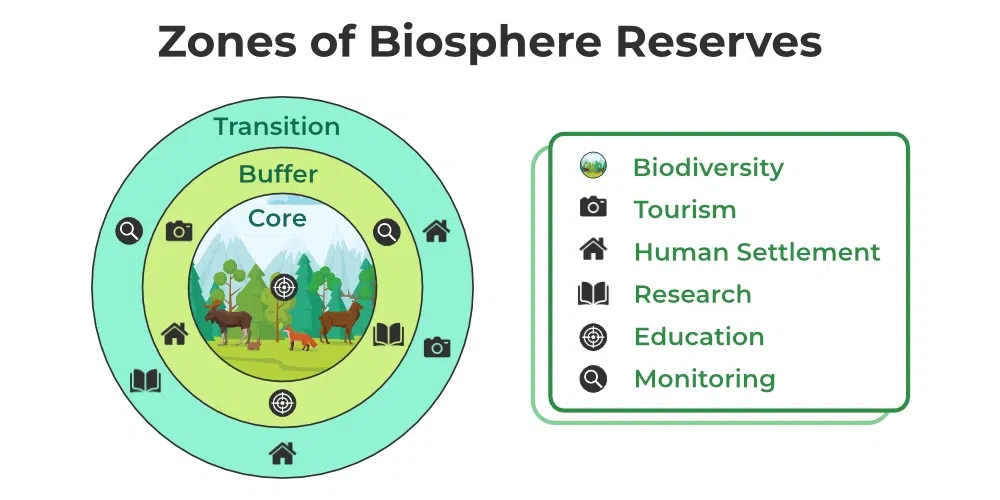
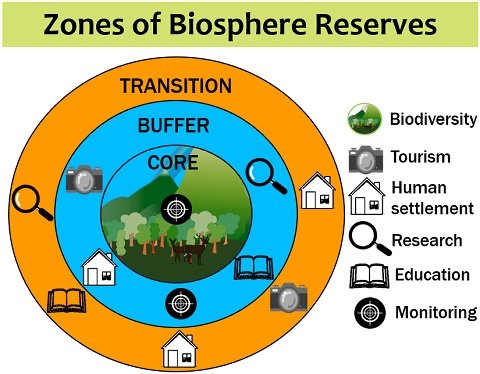
Three Zones of Coexistence:
The core feature of biosphere reserves lies in their zoning system, comprising three distinct areas:
a. Core Area:
This heart of the reserve is a pristine wilderness where human intervention is kept to an absolute minimum. It serves as a sanctuary for endangered species and natural processes, fostering the undisturbed evolution of ecosystems.
b. Buffer Zone:
Encircling the core area, the buffer zone allows for limited human activities that are compatible with conservation goals. Sustainable agriculture, controlled tourism, and eco-friendly practices are often encouraged in this zone.
c. Transition Zone:
As the outermost layer of the reserve, the transition zone accommodates human settlements and economic activities. Here, community participation is crucial to ensure responsible resource management and sustainable development.
Conservation of Biodiversity:
Biosphere reserves play a pivotal role in preserving the rich tapestry of life on Earth. By safeguarding diverse ecosystems, from dense forests to marine habitats, they ensure the survival of countless species. Conservation efforts extend beyond protecting charismatic megafauna to safeguarding intricate webs of plant and animal life that sustain the delicate balance of nature.
Symbiotic Relationship with Local Communities:
Unlike traditional protected areas that often displace local communities, biosphere reserves seek to foster a symbiotic relationship between humans and nature. The involvement of local communities in decision-making processes, sustainable resource utilization, and eco-friendly livelihoods helps to bridge the gap between conservation goals and human needs.
Research and Education:
Biosphere reserves serve as living laboratories, attracting scientists, researchers, and students from around the globe. These areas provide unparalleled opportunities to study complex ecological processes, monitor changes over time, and devise strategies for conservation and sustainable development.
International Collaboration:
The global network of biosphere reserves encourages cross-border collaboration and knowledge exchange. Experiences and lessons learned in one reserve can be shared with others, amplifying conservation efforts and fostering a deeper understanding of environmental challenges faced worldwide.
Which is the first biosphere reserve in India?
The first biosphere reserve in India is the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, which was established in 1986. It is located in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka, in southern India. The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is known for its rich biodiversity, encompassing a wide range of ecosystems, including tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, grasslands, and high-altitude montane forests.
India has 18 Biosphere reserve:
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka)
- Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu)
- Sunderbans Biosphere Reserve (West Bengal)
- Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve (Uttarakhand)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve (Meghalaya)
- Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh)
- Simlipal Biosphere Reserve (Odisha)
- Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve (Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh)
- Manas Biosphere Reserve (Assam)
- Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve (Andaman and Nicobar Islands)
- Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve (Kerala, Tamil Nadu)
- Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve (Sikkim)
- Kanchenjunga Biosphere Reserve (Sikkim)
- Panna Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh)
- Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve (Himachal Pradesh)
- Seshachalam Hills Biosphere Reserve (Andhra Pradesh)
- Pargadh Biosphere Reserve (Maharashtra)
- Similipal Biosphere Reserve (Odisha)
How many biosphere reserve are there in world ?
There are currently 738 biosphere reserves in 134 countries, including 22 transboundary sites, that belong to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. (2023)
3 thoughts on “What is Biosphere Reserve ?”
Your blog has become a part of my daily routine Your words have a way of brightening up my day and lifting my spirits
Your blog has become my daily dose of positivity and inspiration It’s a space that I always look forward to visiting
Your words have the power to change lives and I am grateful for the positive impact you have had on mine Thank you