Devonian Period
Devonian Period: A Dive into Ancient Evolution
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- The Devonian Period: A Time of Transition
- Climate and Geography of the Devonian World
- Flora and Fauna of the Devonian Seas
- 4.1 Age of Fishes: Evolution of Jawed Fishes
- 4.2 Tetrapod Rise: From Water to Land
- 4.3 Ancient Forests: Proliferation of Plants
- Mass Extinction Events and Devonian Decline
- The Devonian’s Impact on Earth’s Geological History
- Conclusion
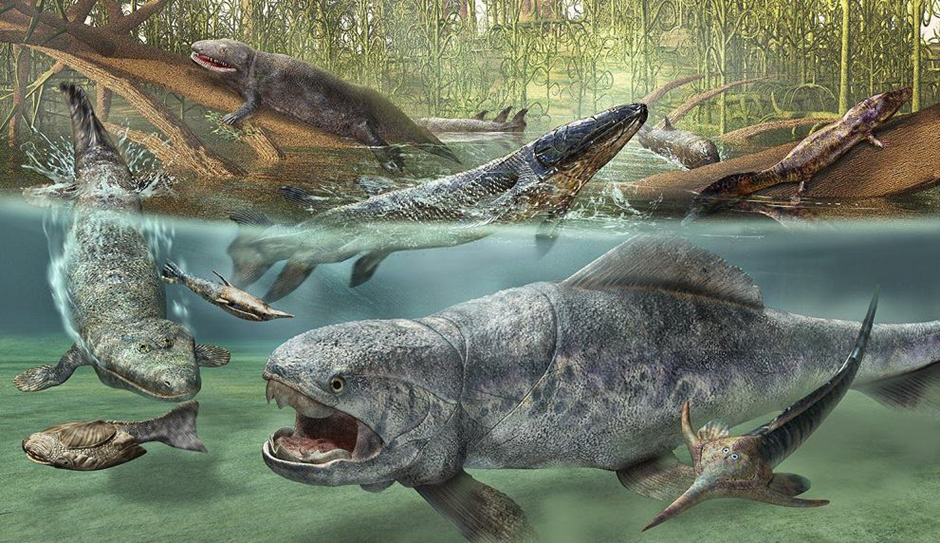
Introduction:
The Devonian Period, spanning from approximately 419 million to 359 million years ago, is often referred to as the “Age of Fishes” and holds a pivotal place in Earth’s evolutionary history. During this remarkable era, life on Earth underwent significant transformations, with the emergence of diverse aquatic creatures, the transition of vertebrates from water to land, and the rise of ancient forests. In this article, we will embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of the Devonian Period, exploring its unique characteristics, its impact on life forms, and its contribution to our planet’s geological timeline.
The Devonian Period: A Time of Transition:
The Devonian Period marked a transitional phase in Earth’s history, bridging the gap between the Silurian and Carboniferous periods. It witnessed significant evolutionary innovations, including the rise of various aquatic and terrestrial life forms that played a crucial role in shaping the world’s ecosystems.
Climate and Geography of the Devonian World:
During the Devonian Period, Earth’s climate was relatively warm and tropical, with extensive shallow seas and continents drifting towards the equator. The presence of warm ocean currents and abundant sunlight supported the proliferation of diverse marine life forms and lush terrestrial ecosystems.
Climate: Warm and Tropical Conditions
During the Devonian Period, the Earth experienced a relatively warm and tropical climate, which had a profound impact on both terrestrial and marine environments.
Tropical Ocean Currents:
Warm ocean currents flowed across the planet’s oceans, contributing to the overall warmth of the Devonian climate. These currents helped regulate temperatures and provided a hospitable environment for marine life to thrive. The equatorial regions were particularly warm, with sea temperatures conducive to the proliferation of diverse marine ecosystems.
Greenhouse Effect:
The Devonian climate is often described as a greenhouse world due to elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This enhanced greenhouse effect led to higher global temperatures and facilitated the expansion of tropical environments. The increased CO2 levels also contributed to the warming of oceans and the subsequent diversification of marine life.
Geography: Shifting Continents and Expanding Oceans
The geographic landscape of the Devonian world underwent significant changes, influencing the distribution of species and the formation of different habitats.
Continental Drift:
During the Devonian Period, the continents were in the process of drifting towards the equator, resulting in the assembly of the supercontinent Gondwana. This movement altered oceanic circulation patterns and influenced the distribution of warm ocean currents. The shifting continents also led to the formation of new ocean basins, providing diverse marine habitats for evolving life forms.
Shallow Seas and Coastlines:
The Devonian saw the expansion of shallow seas and the development of extensive coastlines. These shallow marine environments were teeming with life, including various marine invertebrates and early fish species. The presence of shallow waters allowed for the proliferation of diverse marine ecosystems, contributing to the “Age of Fishes.”
Terrestrial Habitats:
On land, the Devonian witnessed the proliferation of plant life, leading to the formation of ancient forests and terrestrial ecosystems.
Flora and Fauna of the Devonian Seas:
The Devonian seas were home to a rich diversity of life forms, contributing to its nickname as the “Age of Fishes.” Key developments during this period include:
4.1 Age of Fishes: Evolution of Jawed Fishes:
The Devonian witnessed a significant milestone in vertebrate evolution—the emergence of jawed fishes. These creatures, equipped with powerful jaws and enhanced feeding abilities, diversified into various lineages, laying the foundation for the later evolution of modern fish species.
4.2 Tetrapod Rise: From Water to Land:
One of the most pivotal events in Devonian history was the transition of vertebrates from aquatic environments to land. Tetrapods, the earliest land-dwelling vertebrates, evolved from their fish ancestors and ventured onto the terrestrial landscape, adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
4.3 Ancient Forests: Proliferation of Plants:
The Devonian also witnessed the proliferation of plant life, with the emergence of diverse terrestrial ecosystems. Ancient forests comprised various plant species, including early ferns and primitive trees, which played a vital role in stabilizing soil, influencing climate patterns, and providing habitats for terrestrial animals.
Mass Extinction Events and Devonian Decline:
Towards the end of the Devonian Period, the world experienced several mass extinction events, leading to the decline of numerous marine species. While the causes of these extinctions are complex and debated, they set the stage for new evolutionary trajectories in the subsequent geological periods.
The Devonian’s Impact on Earth’s Geological History:
The Devonian Period had a lasting impact on Earth’s geological history. Sediment deposits from this time, such as limestone and shale, are rich in fossils and provide valuable insights into the ancient life forms that inhabited our planet.
Conclusion:
The Devonian Period stands as a testament to the dynamic nature of Earth’s ecosystems and the continuous evolution of life. From the emergence of jawed fishes to the transition of vertebrates onto land and the proliferation of ancient forests, the Devonian Period marked a time of transformation and innovation. By studying this period, we gain a deeper understanding of the origins of modern ecosystems, the evolutionary paths of diverse life forms.