Lion: Taxonomy, worldwide population, species, conservation status
Table of Content:
Introduction
Taxonomy and classification
Species
Habitat, Diet, Behavior
Conservation Status
Worldwide population of lions (Panthera leo)
Which country has highest population of lions?
Lifespan
Gestation period
Offspring
Conservation Efforts
Conservation Initiatives
Introduction:
In the vast tapestry of the African and select Asian landscapes, one majestic creature stands as an icon of regality and raw power—the lion (Panthera leo). With its imposing presence, impressive manes, and resonant roars that echo through the savannas, the lion commands reverence as the undisputed king of the animal kingdom.
Taxonomy and classification:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Subphylum: Vertebrata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Genus: Panthera
- Species: Panthera leo

Species:
The term “lion” typically refers to a single species, Panthera leo. However, within this species, there are several recognized subspecies, each with its own distinct characteristics.
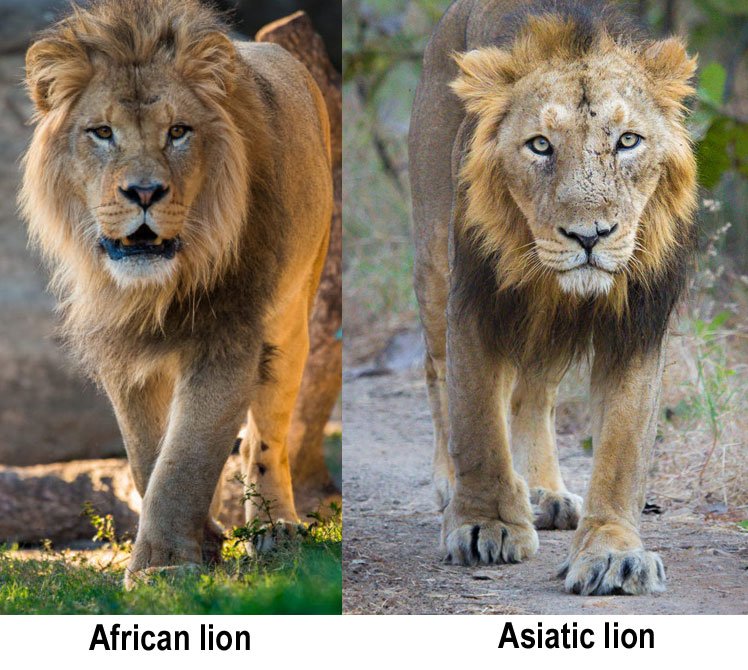
Panthera leo leo (African Lion): This subspecies is found in various regions across Africa, and its populations are distributed in different countries.
Panthera leo persica (Asiatic Lion): The Asiatic lion is a subspecies found in a small population in the Gir Forest National Park in India.

Habitat:
Lions are highly adaptable big cats that inhabit a range of environments, primarily found in savannahs, grasslands, and open woodlands. They are also known to dwell in semi-arid regions. The availability of cover, water sources, and prey are critical factors influencing their choice of habitat. Lions are primarily indigenous to sub-Saharan Africa, with a small population of Asiatic lions found in the Gir Forest National Park in India.
Diet
As apex predators, lions are carnivores with a diverse diet. Their primary prey consists of herbivores such as wildebeest, zebras, and antelopes. Lions are opportunistic hunters, capable of taking down large ungulates through coordinated group efforts. The hunting strategy often involves stalking, ambushing, and working together to bring down prey. Lions are also known to scavenge, taking advantage of the kills made by other predators when the opportunity arises.
Behavior:
Territorial Behavior
Lions are territorial animals, and the pride establishes and defends a designated territory. Territorial markings, including scent markings and vocalizations such as roars, serve to communicate boundaries and warn intruders. Territories provide crucial resources such as ample prey, water sources, and shelter.
Reproductive Behavior
Reproductive behavior in lions is tied to the social structure of prides. Dominant males mate with multiple females within the pride. Lionesses synchronously come into estrus, leading to a synchronized breeding pattern. Cubs are born after a gestation period of approximately 3.5 months, and the entire pride contributes to the care and protection of the young.
Nocturnal Activity
Lions are crepuscular and nocturnal hunters, meaning they are most active during dawn and dusk. This behavior is advantageous for avoiding the intense heat of the day and capitalizing on the cover of darkness for hunting. Their acute night vision and well-developed sense of hearing contribute to their effectiveness as nocturnal predators.

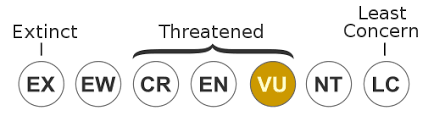
Conservation Status
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies lions under the following categories:
- Species: Panthera leo
- IUCN Red List Status: Vulnerable
lions (Panthera leo) are classified as “Vulnerable” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. The “Vulnerable” status indicates that lions are facing a high risk of extinction in the wild.
Worldwide population of lions (Panthera leo):
Estimating the exact worldwide population of lions (Panthera leo) is a challenging task due to the vast and often remote habitats they inhabit across Africa and a small population in India. However, it is estimated that there are approximately 30,000 to 100,000 (2023) lions in the wild.
Which country has highest population of lions?
The highest population of lions is in South Africa ( Tanzania, Kenya, and Botswana ).

Lifespan
Wild Lifespan: In the wild, lions generally have a lifespan of about 10 to 14 years. However, various factors, including the availability of prey, competition with other predators, and environmental conditions, can influence their longevity.
Captive Lifespan: Lions in captivity tend to live longer, with some individuals reaching up to 20 years or more. The controlled environment, access to veterinary care, and a consistent food supply contribute to their extended lifespans.

Gestation period:
The gestation period for lions (Panthera leo) is approximately 110 days. This period represents the time between conception and the birth of the cubs.
Offspring:
Lions (Panthera leo) typically give birth to a litter of cubs. The average size of a lioness’s litter ranges from 2 to 4 cubs. However, the exact number can vary, and litters of up to 6 cubs have been documented in some cases.

Conservation Efforts:
Protected Areas
Efforts to mitigate conflict often involve the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves. Creating spaces where lions can thrive without direct competition with human activities is essential.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives is vital. This can include education programs, establishing community-based conservation projects, and developing strategies to minimize the impact of lion presence on local livelihoods.

Conservation Initiatives
Efforts to conserve lions and their habitats are multifaceted, involving local communities, governments, and international organizations. Key initiatives include:
Protected Areas and Reserves
Community-Based Conservation
Anti-Poaching Measures
Research and Monitoring
