What Is Ovoviviparous Animals ?
Ovoviviparity:
“Ovoviviparous” is another mode of reproduction found in certain animals, combining aspects of both oviparity and viviparity. In ovoviviparous reproduction:
Fertilization:
Fertilization usually occurs internally, with the male depositing sperm inside the female’s reproductive tract. After fertilization, the embryos develop within eggs inside the female’s body. These eggs are retained and kept internally, providing a protected environment for embryonic development. The yolk of the egg serves as a nutrient source for the developing embryos during this internal phase.
Embryo Development:
Unlike oviparous animals where eggs are laid outside the body, in ovoviviparous animals, the embryos develop within eggs. However, these eggs are retained inside the female’s body. After fertilization, the developing embryos are encapsulated within eggs. These eggs have protective membranes and contain the necessary nutrients, usually in the form of yolk, for the growing embryos.
Instead of laying the eggs externally, as in oviparous reproduction, the female retains the eggs inside her body. The eggs may be held within specialized structures or chambers.
Nourishment:
The embryos are nourished by the yolk of the egg, which provides the necessary nutrients for their development. Unlike viviparity, there is no direct maternal connection for nutrient exchange.
Egg Protection:
While the eggs are inside the female’s body, they are protected from external environmental factors, providing a safer environment for embryonic development compared to external egg-laying.
Birth:
The offspring are born live, but the birth process is different from viviparity. The young hatch from the eggs inside the mother’s body, and then they are born as live young. This is in contrast to viviparous animals where the young are born live without an external egg.
Examples:
Sharks and Rays: Many species of sharks, such as the hammerhead shark, and some types of rays follow an ovoviviparous reproductive strategy.
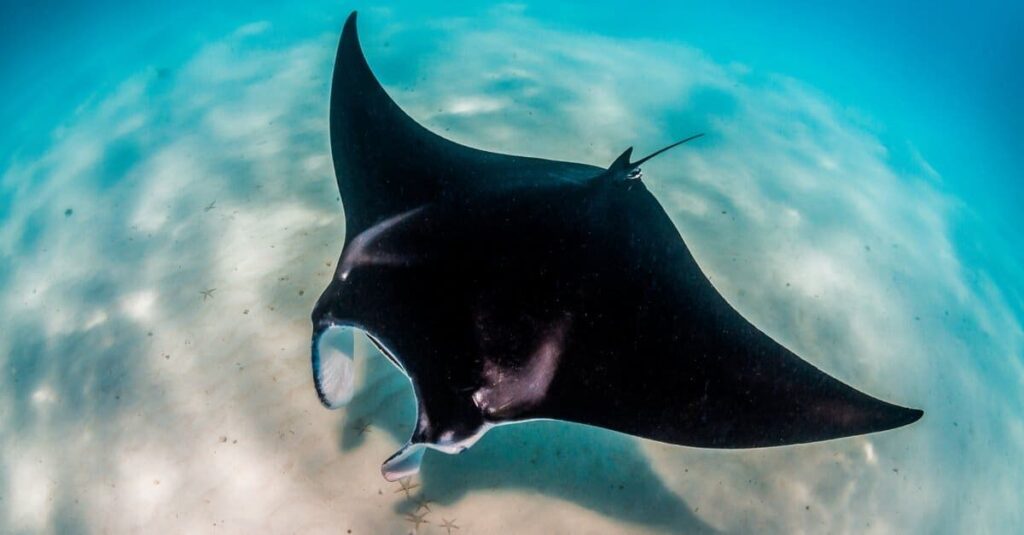
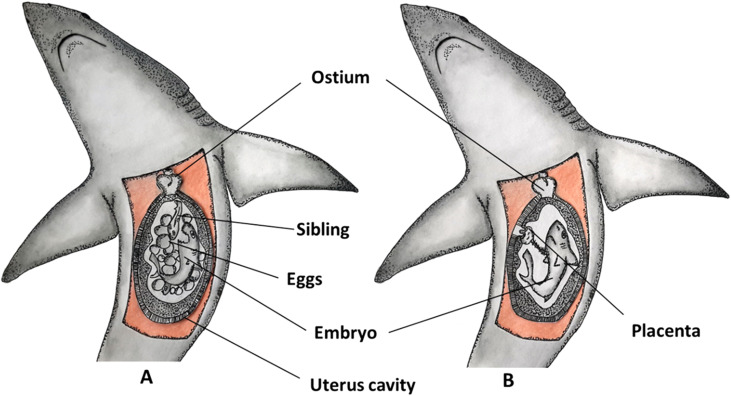



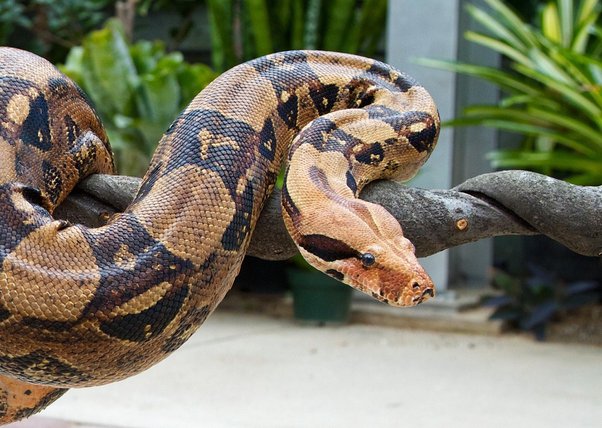
Snakes: Certain snakes, including boa constrictors and some vipers, exhibit ovoviviparity.

Insects: Some insects, like certain species of cockroaches, also reproduce through ovoviviparity.

Advantages and Adaptations:
Protection of Offspring: Ovoviviparity offers a level of protection to the developing embryos, as they are shielded within the mother’s body until they are ready to hatch.
Safer Environment: Compared to oviparity, where eggs may be vulnerable to predation or environmental conditions, ovoviviparity provides a more controlled and safer environment for embryonic development.
Increased Survival: By giving birth to live young, ovoviviparous animals may increase the chances of survival for their offspring compared to those that rely on external egg-laying.
In summary, ovoviviparity represents a reproductive strategy that combines elements of both oviparity and viviparity. The embryos develop within eggs, which are retained inside the mother’s body until they hatch, leading to the birth of live offspring. This strategy offers a balance between protection and a safer environment for embryonic development.
2 thoughts on “What Is Ovoviviparous Animals ?”
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. kudos
This site is known as a walk-by way of for the entire info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and also you’ll definitely discover it.