
Tiger Reserves in India
INTRODUCTION :
The tiger reserves provide a safe and secure habitat for the Bengal tiger and other wildlife species, and the conservation efforts carried out in these reserves have helped to increase the tiger population in India. The reserves also offer visitors a chance to see these majestic animals in their natural habitat, promoting eco-tourism in the country.
The establishment of tiger reserves in India was a significant step towards the conservation of the endangered Bengal tiger and its habitat. India has a long history of wildlife conservation, and the government’s decision to establish tiger reserves under the Project Tiger initiative in 1973 was a major milestone in these efforts.
The history of tiger reserves in India can be traced back to the early 20th century when the tiger population began to decline rapidly due to hunting and habitat loss. In response, the government of India took several steps to protect the species and its habitat.
One of the most significant conservation efforts was the launch of Project Tiger in 1973. This project aimed to protect the Bengal tiger and its habitat by establishing tiger reserves throughout India. The first nine tiger reserves were established under Project Tiger in 1973, and additional reserves have been established since then.
Tiger Reserves in india :
India has 51 tiger reserves spread across 18 states, covering a total area of 72,749 sq km. Here is a list of some of the most popular tiger reserves in India:
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh
- Kanha Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh
- Sunderbans Tiger Reserve, West Bengal
- Sariska Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan
- Pench Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve, Maharashtra
- Periyar Tiger Reserve, Kerala
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan
- Satpura Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh
- Nagzira Wildlife Sanctuary and Tiger Reserve, Maharashtra

In India there are only one type of tiger species, that is:
Royal Bengal Tiger :
The Bengal tiger, also known as the Royal Bengal Tiger, is a subspecies of tiger native to the Indian subcontinent. Its scientific name is Panthera tigris tigris.
Bengal tigers have a long and rich history. They have been revered in Indian culture for centuries and were often depicted in ancient Indian art and literature. Historically, they were also used as hunting animals by Indian kings and nobility.

The Bengal tiger is one of the most iconic and magnificent animals in India and is an important cultural and ecological symbol in the country. It is the national animal of India and is featured in several Indian folktales and traditions.
In addition to the Bengal tiger, India is also home to another subspecies of tiger known as the Indochinese tiger (Panthera tigris corbetti). However, the Indochinese tiger is very rare in India and is found only in a few pockets along the Indo-Myanmar border.
Population:
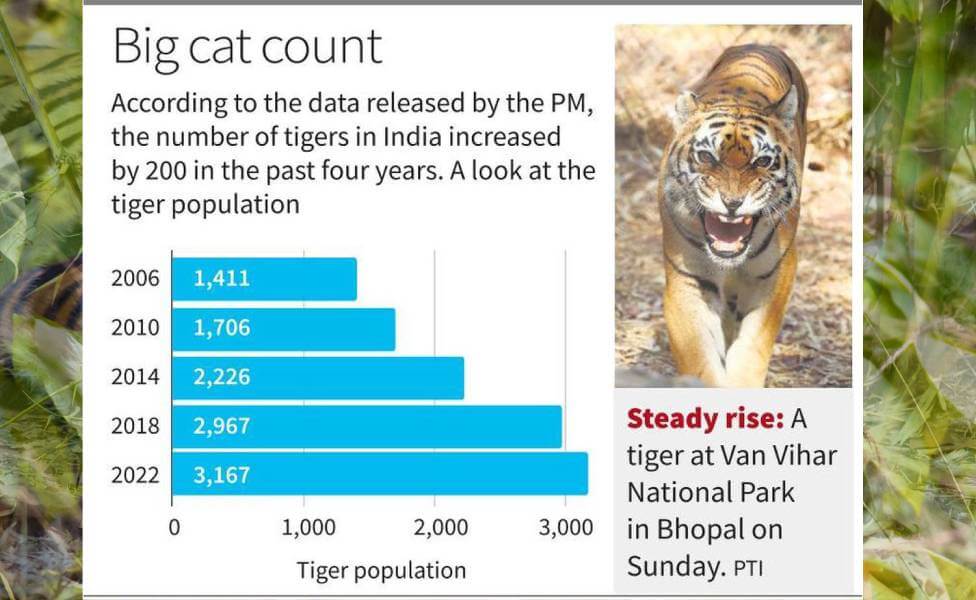
Population has grown by 200 from 2018 to 2022. The current tiger population in India is 3,167, up from 2,967 in 2018. The national tiger census is done every four years by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
One thought on “Tiger Reserves in India”
Your blog has really piqued my interest on this topic. Feel free to drop by my website UY8 about Thai-Massage.